Footage Of Worlds Largest Iceberg Splitting From Antarctica
This footage shows the world’s largest existing iceberg splitting from Antarctica earlier this month.
Satellites of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) filmed the iceberg, named A-76, splitting from the Ronne Ice Shelf on 15th and 16th May.
NOAA posted the video on social media on 28th May with the message: “An iceberg nearly the size of Delaware sheared off from the edge of Antarctica earlier this month and floated into the Weddell Sea, where it is now starting to fracture into pieces.
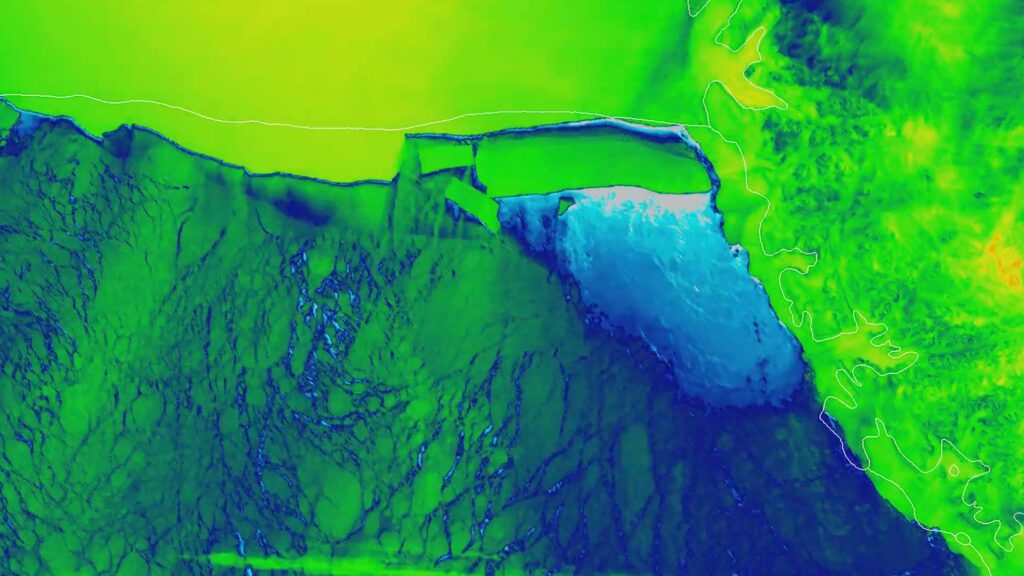
“The iceberg, named A-76 by the US National Ice Center, measured 1,668 square miles before breaking up.
“The Joint Polar Satellite System’s polar-orbiting satellites observed A-76 splitting from the Ronne Ice Shelf on 15th and 16th May during multiple flyovers.”
Dr Jeff Key of the National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service (NESDIS), created by the NOAA to operate US environmental satellite programmes, said the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) plays an important role in monitoring glaciers as well as measuring the surface albedo and temperature of ice sheets, ice concentration, and motion of sea ice.
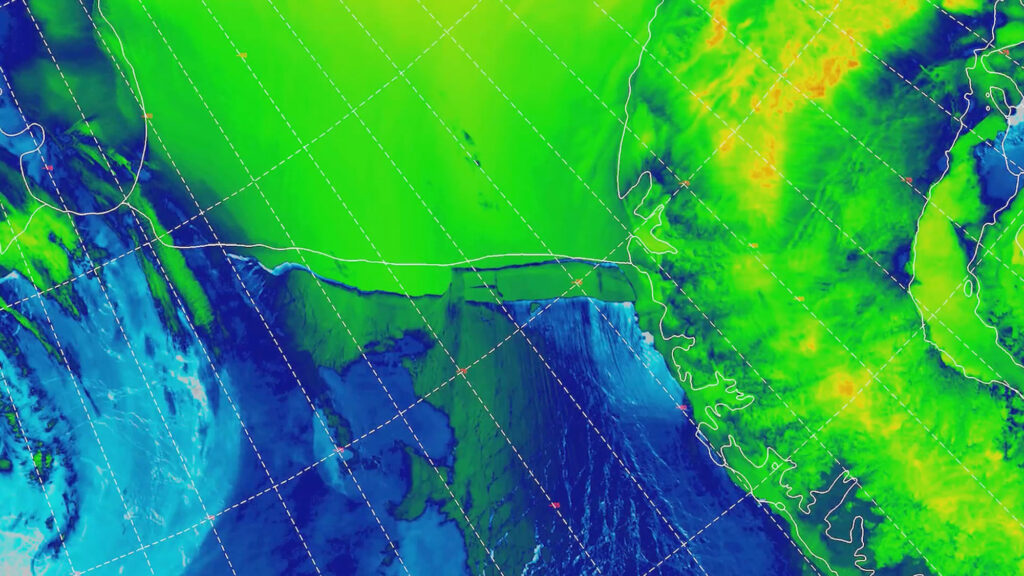
Dr Key added: “Because A-76 is floating ice, it won’t raise the sea level.
“It’s like ice cubes in your drink, when they melt, they don’t cause the glass to overflow.
He explained that warm water melts the underside of the ice shelf over time, causing it to slowly break up.
At the same time, meltwater on the surface of the iceberg percolates through cracks and further erodes the ice.
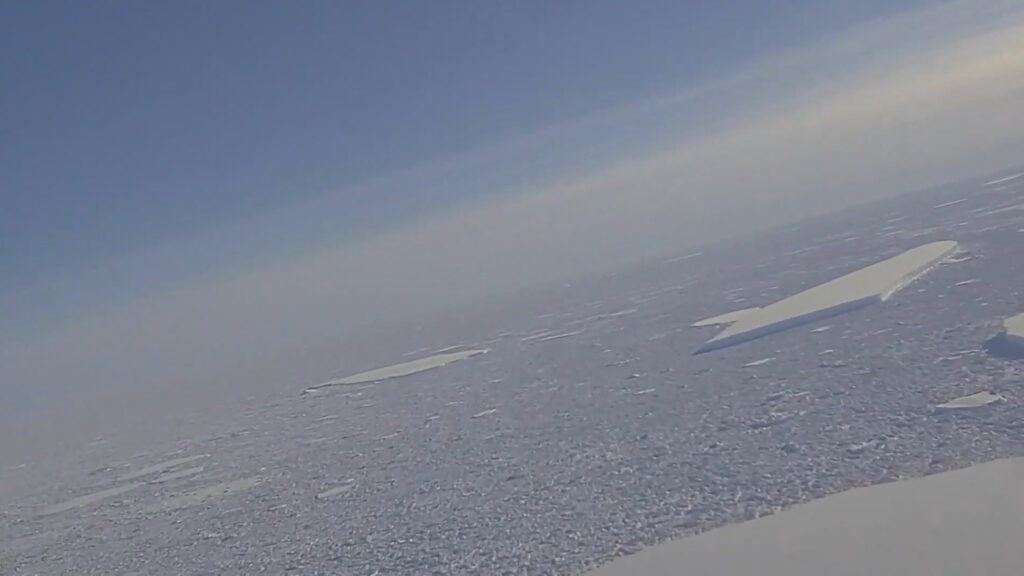

Dr Kelly Brunt of the Cryospheric Sciences Laboratory at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center said: “Along the flanks, there are a lot more ‘rift precursors’ or fractures in the ice, due to the proximity to the shear margins. Those fractures could easily lead to more breakup.”
The largest recorded iceberg was the B-15, measuring 4,200 square miles. It split from Antarctica’s Ross Ice Shelf in March 2000 and gradually broke up into smaller pieces.
The Suomi-NPP and NOAA-20 satellites orbit the Earth at an altitude of 512 miles, providing high-resolution images and gauging temperatures and moisture measurements.



